Quantifying Heteroscedasticity in Ordinary Least Squares Models
Sladekova, M., Field, A. P.
Stage: Manuscript in preparation
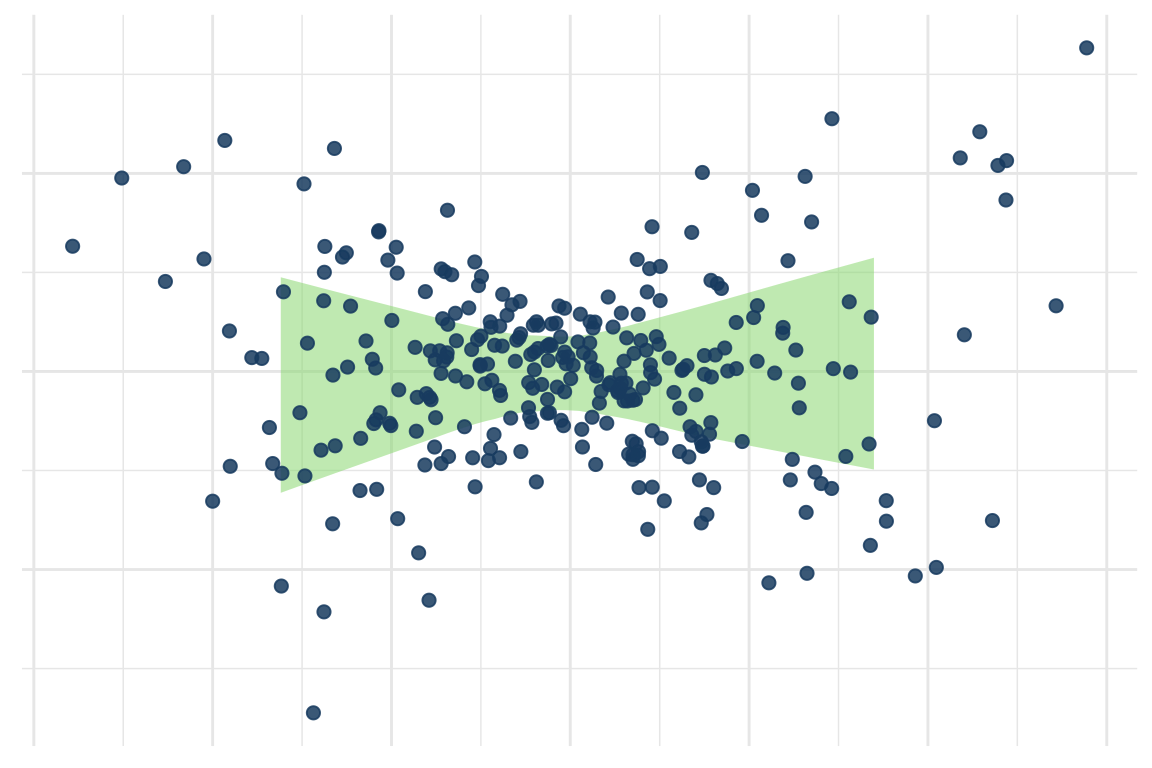
Non-constant variance can cause issues for hypothesis testing when using OLS models, including loss of statistical power or the increase in the frequency of false-positive findings. In models with categorical predictors, the extent of heteroscedasticity can be quantified with a ratio variance across different groups. In designs with continuous predictors however, no method with intuitive interpretation is readily available.
Throughout the course of this simulation study, we have developed a method which constructs an interval around the distribution of the residuals as a function of the values of the predictor(s) and estimates the change in the width of the interval using polynomial terms in a linear model. This way, different shapes of heteroscedasticity can be captured and quantified.